Architecture
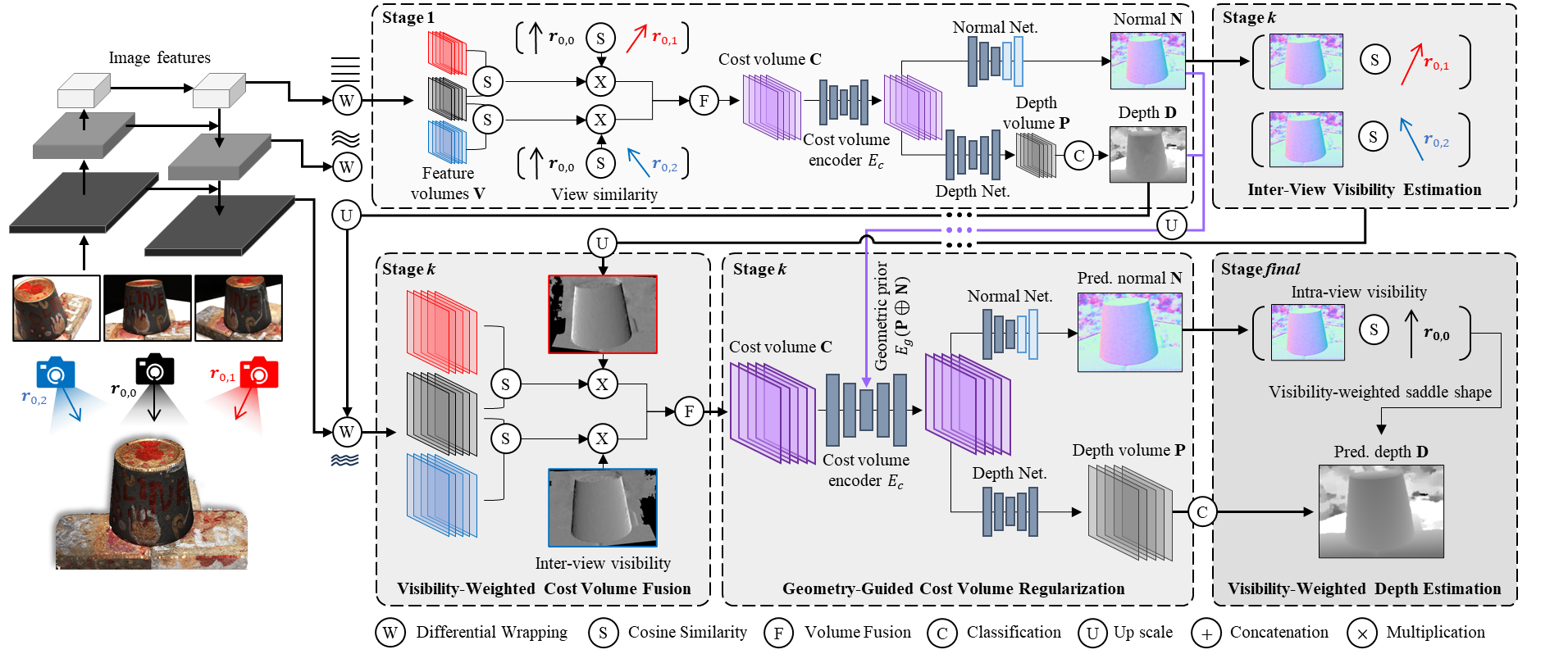

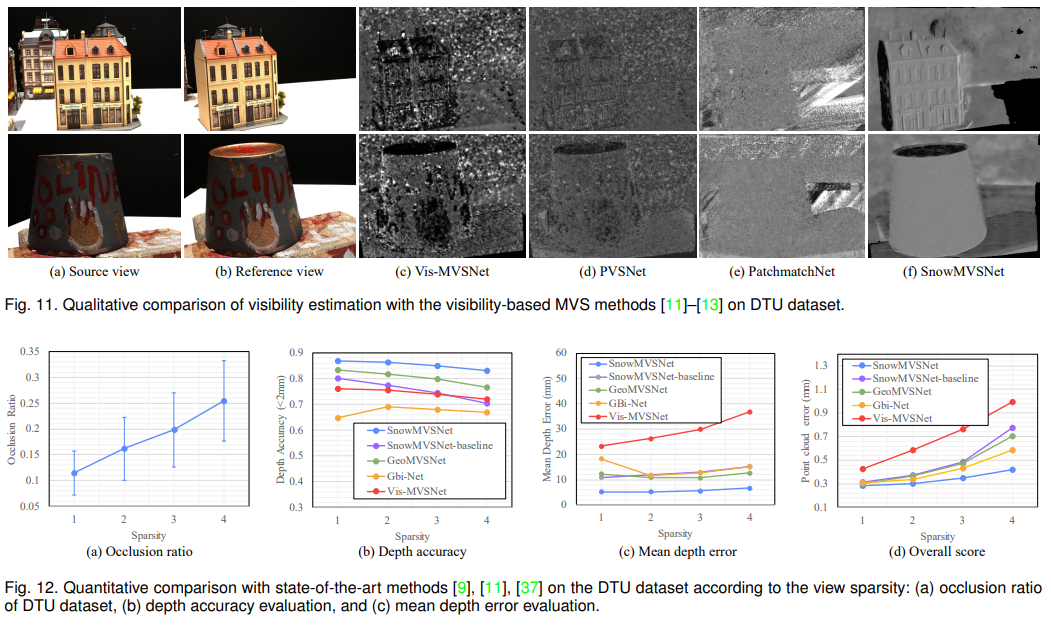
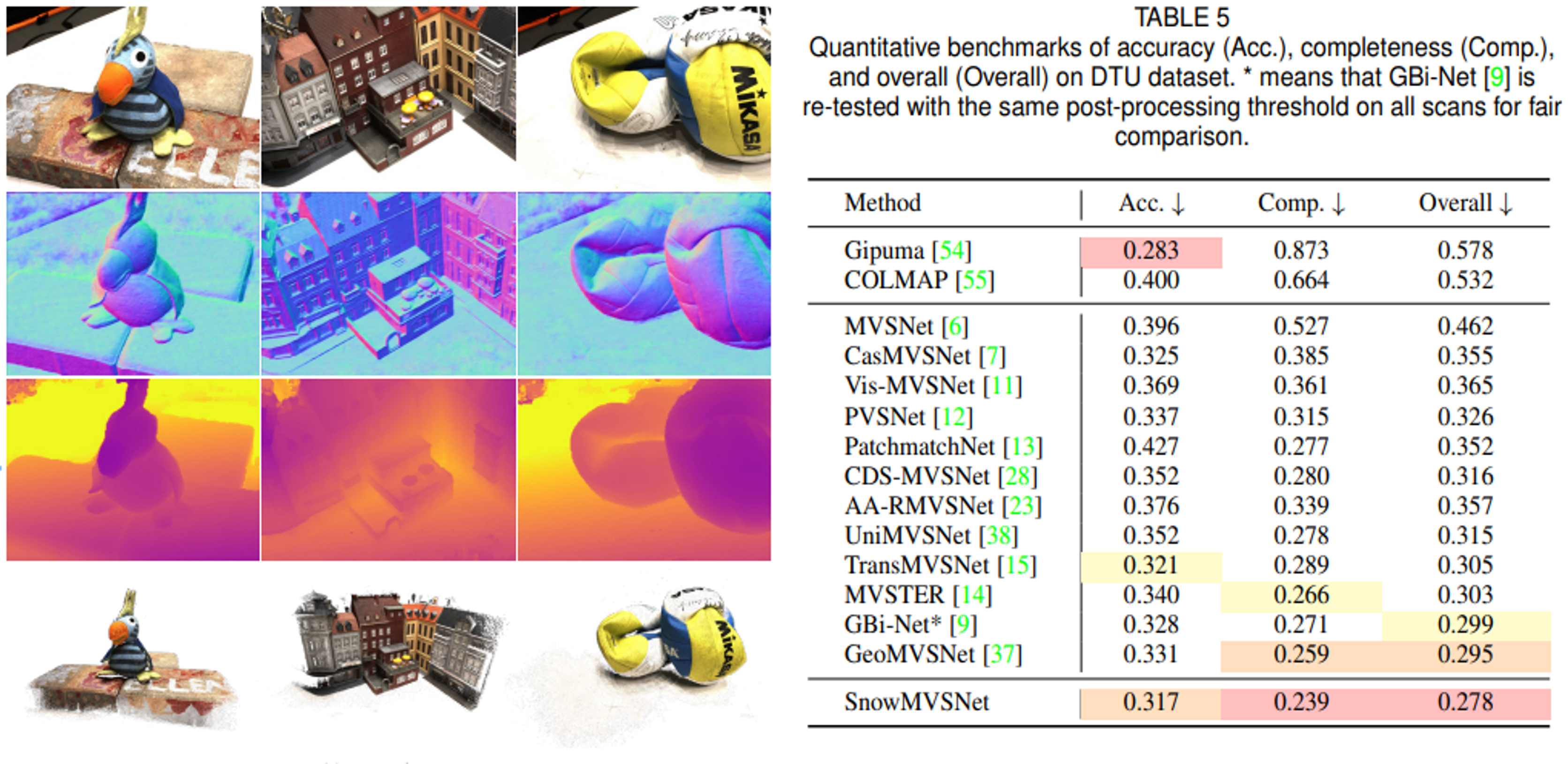
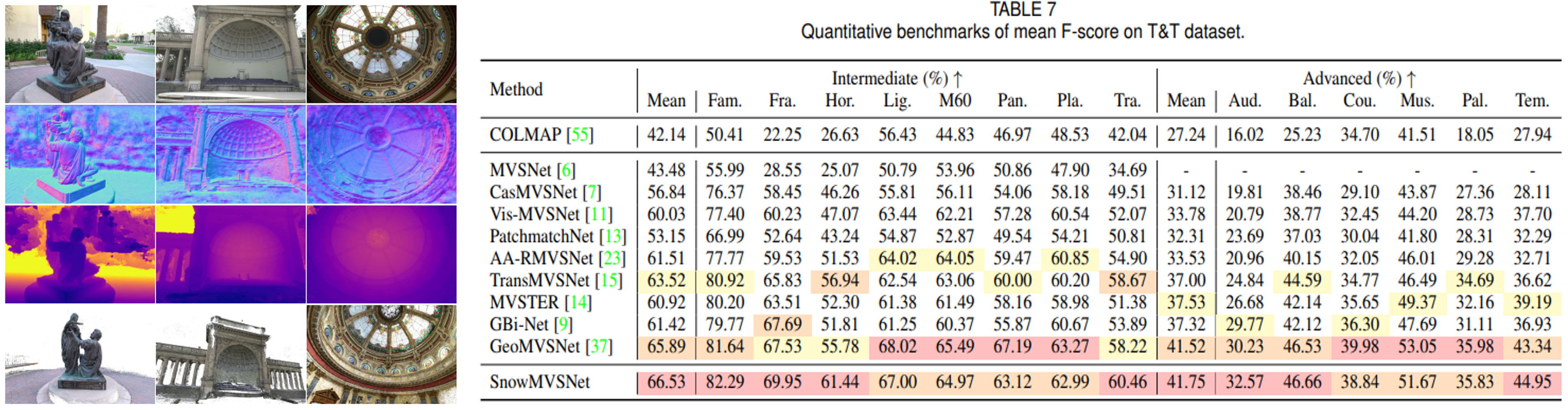
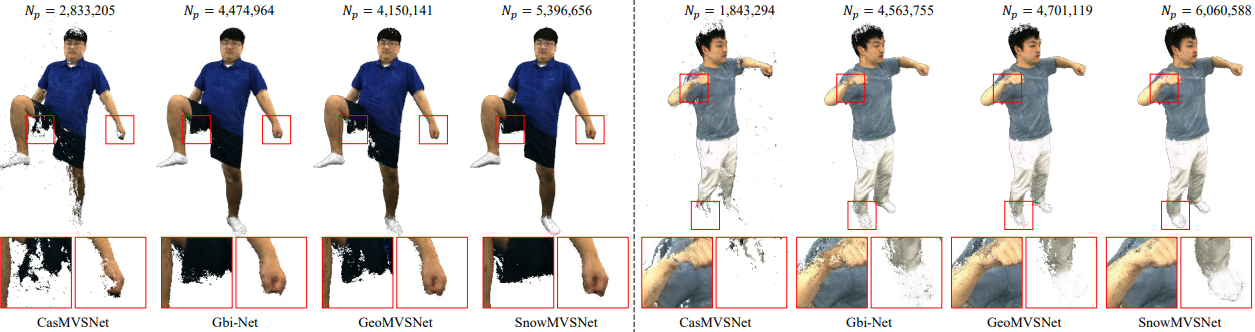
Recent learning-based multi-view stereo (MVS) still exhibits insufficient accuracy in large occlusion cases, such as environments with significant inter-camera distance or when capturing objects with complex shapes. This is because incorrect image features extracted from occluded areas serve as significant noise in the cost volume construction. To address this, we propose a visibilityaware MVS using surface normal weighting (SnowMVSNet) based on explicit 3D geometry. It selectively suppresses mismatched features in the cost volume construction by computing inter-view visibility. Additionally, we present a geometry-guided cost volume regularization that enhances true depth among depth hypotheses using a surface normal prior. We also propose intra-view visibility that distinguishes geometrically more visible pixels within a reference view. Using intra-view visibility, we introduce the visibility-weighted training and depth estimation methods. These methods enable the network to achieve accurate 3D point cloud reconstruction by focusing on visible regions. Based on simple inter-view and intra-view visibility computations, SnowMVSNet accomplishes substantial performance improvements relative to computational complexity, particularly in terms of occlusion robustness. To evaluate occlusion robustness, we constructed a multi-view human (MVHuman) dataset containing general human body shapes prone to self-occlusion. Extensive experiments demonstrated that SnowMVSNet significantly outperformed state-of-the-art methods in both low- and highocclusion scenarios.
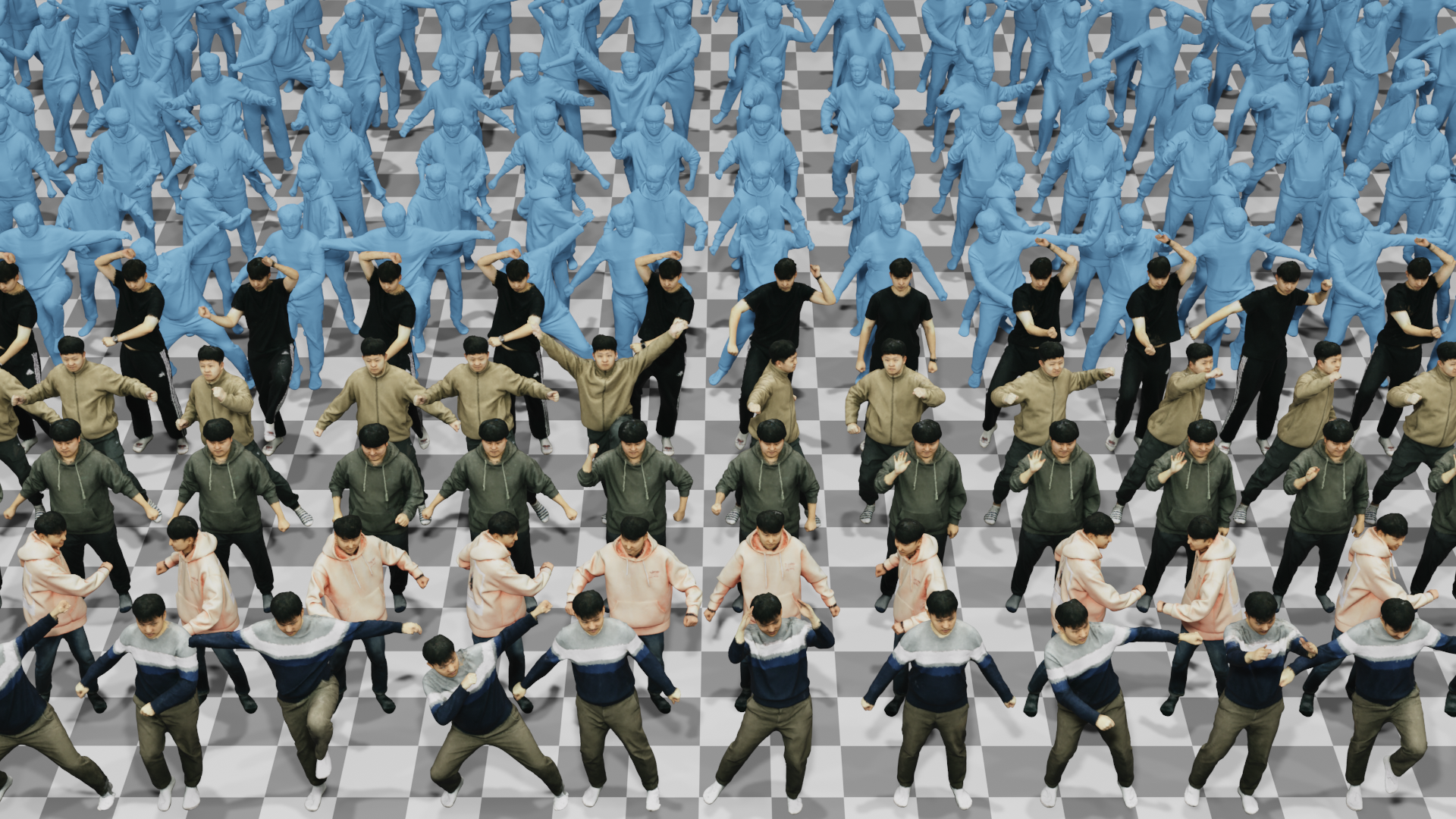

We offer multiview human data from SnowMVSNet, including images, depths, normals, camera matrix and meshes for 5 subjects across 10 different poses.